Disruption of RFX family transcription factors
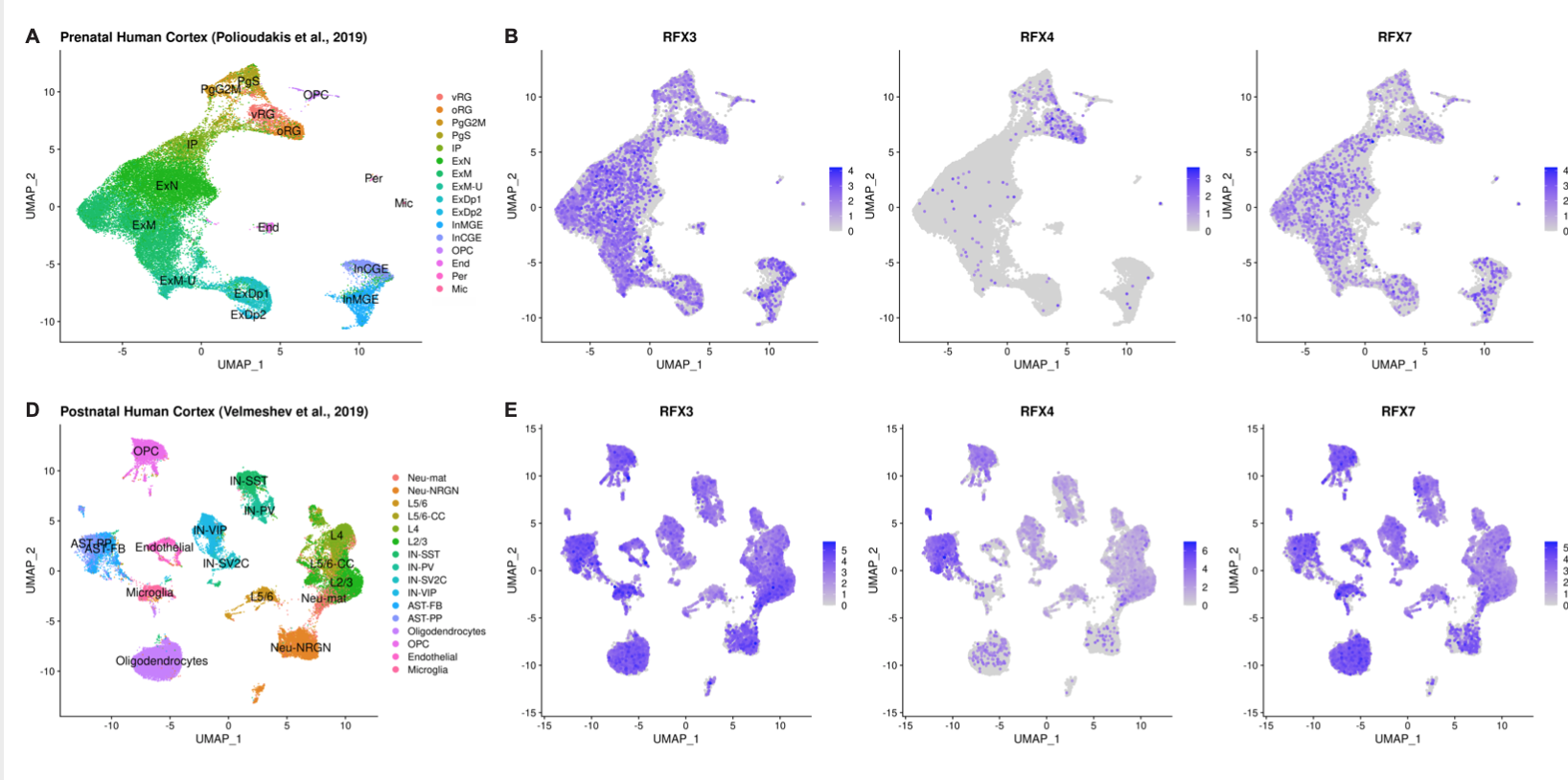
Our recent study delineates a novel human neurobehavioral phenotype including ASD, ID, and/or ADHD due to deleterious variants in RFX family transcription factors in 38 individuals. This report complements accumulating statistical genetic evidence for RFX3 as an ASD risk gene and extends these findings to the closely related RFX family members RFX4 and RFX7. We show that the RFX members are highly expressed in the developing and adult cortex and likely regulate the expression of other neurodevelopment risk genes. Read more in our Genetics in Medicine paper. rdcu.be/cf8i7